Depletion Mode Mosfet
A P-Channel MOSFET is a type of MOSFET in which the channel of the MOSFET is composed of a majority of holes as current carriers. When the MOSFET is activated and is on, the majority of the current flowing are holes moving through the channels.
In most circuits, this means pulling an enhancement-mode MOSFET's gate voltage towards its drain voltage turns it ON. In a depletion-mode MOSFET, the device is normally ON at zero gate–source voltage. Such devices are used as load 'resistors' in logic circuits (in depletion-load NMOS logic, for example). The DN2470 is a low threshold depletion-mode (normally-on) transistor utilizing an advanced vertical DMOS structure and well-proven silicon-gate manufacturing process.
This is in contrast to the other type of MOSFET, which are N-Channel MOSFETs, in which the majority ofcurrent carriers are electrons.
Before, we go over the construction of P-Channel MOSFETs, we must go over the 2 types that exist. There are 2 types of P-Channel MOSFETs, enhancement-type MOSFETs and depletion-type MOSFETs.
A depletion-type MOSFET is normally on (maximum current flows from source to drain) when no differencein voltage exists between the gate and source terminals. However, if a voltage is applied to its gate lead, the drain-source channel becomes more resistive, until the gate voltage is so high, the transistor completely shuts off. An enhancement-type MOSFET is the opposite. It is normally off when the gate-source voltage is 0V(VGS=0). However, if a voltage is applied to its gate lead, the drain-source channel becomesless resistive.
In this article, we will go over how both P-Channel enhancement-type and depletion-type MOSFETs are constructed and operate.
How P-Channel MOSFETs Are Constructed Internally
An P-Channel MOSFET is made up of a P channel, which is a channel composed of a majority of hole current carriers. The gate terminals are made up of N-type material.
Depending on the voltage quantity and type (negative or positive)determines how the transistor operates and whether it turns on or off.
How a P-Channel Enhancement-type MOSFET Works
How to Turn on a P-Channel Enhancement Type MOSFET
To turn on a P-Channel Enhancement-type MOSFET, apply a positive voltage VS to the source of the MOSFET and apply a negative voltage to the gate terminal of the MOSFET (the gate must be sufficiently more negative than the threshold voltage across the drain-source region(VG
So with a sufficient positive voltage, VS, to the source and load, and sufficient negative voltage applied to the gate, the P-Channel Enhancement-type MOSFET is fully functional and is in the active 'ON' mode of operation.
How to Turn Off a P-Channel Enhancement Type MOSFET
To turn off a P-channel enhancement type MOSFET, there are 2 steps you can take. You can either cut off the bias positive voltage, VS, that powers the source. Or you can turn off the negative voltagegoing to the gate of the transistor.
How a P-Channel Depletion-type MOSFET Works
How to Turn on a P-Channel Depletion Type MOSFET
To turn on a P-Channel Depletion-Type MOSFET, for maximum operation, the gate voltage feeding the gate terminal should be 0V. With the gate voltage being 0V, the drain current is at is largest value and the transistor is in the active 'ON'region of conduction.
So, again, to turn on a P channel depletion-type MOSFET, positive voltage is applied to the source of the p-channel MOSFET. So we power the source terminal of the MOSFET with VS, a positive voltage supply. With a sufficient positive voltage, VS, and no voltage (0V) applied to the base, the P-channel Depletion-type MOSFET is in maximum operation and has the largest current.
How to Turn Off a P-Channel Depletion Type MOSFET
To turn off a P-channel MOSFET, there are 2 steps you can take. You can either cut off the bias positivevoltage, VDD, that powers the drain. Or you can apply a negative voltage to the gate. When a negativevoltage is applied to the gate, the current is reduced. As the gate voltage, VG, becomes more negative, the current lessens until cutoff, which is when then MOSFET is in the 'OFF' condition. This stops a large source-drain current.
So ,again, as negative voltage is applied to the gate terminal of the P channel depletion-type MOSFET, the MOSFET conducts less and less current across the source-drain terminal. When the gate voltage reaches a certain negative voltage threshold, it shuts the transistor off. Negative voltage shuts the transistor off. This is for a depletion-type P-channel MOSFET.
MOSFET transistors are used for both switching and amplifying applications. MOSFETs are perhaps the most popular transistors used today. Their high input impedance makes them draw very little input current, they are easy to make, can be made very small, and consume very little power.
Related Resources
How to Build a P-Channel MOSFET Switch Circuit
N-Channel MOSFET Basics
N Channel JFET Basics
P Channel JFET Basics
Types of Transistors
difference between Depletion MOSFET vs Enhancement MOSFET
This page on Depletion MOSFET vs Enhancement MOSFET mentions difference between Depletion MOSFET and Enhancement MOSFET.
Depletion MOSFET
Figure-1 depicts construction of depletion type MOSFET. It also mentions circuit symbol of N-channel MOSFET of depletion type.Due to its construction if offers very high input resistance (about 1010 to 1015).Significant current flows for given VDS at VGS of 0 volt.
When gate(i.e. one plate of capacitor) is made positive, the channel((i.e. the other plate of capacitor) will have positive chargeinduced in it. This will result into depletion of majority carriers(i.e. electrons) and hence reduction inconductivity. Hence the curve similarto JFET is obtained as shown in the figure-2.
As shown in the symbol here gate is insulated from the channel.For P-channel type MOSFET symbol, arrow will be reversed.
Figure-2 depicts drain characteristics and transfer curve of depletion type of MOSFET(N-channel).
Enhancement MOSFET

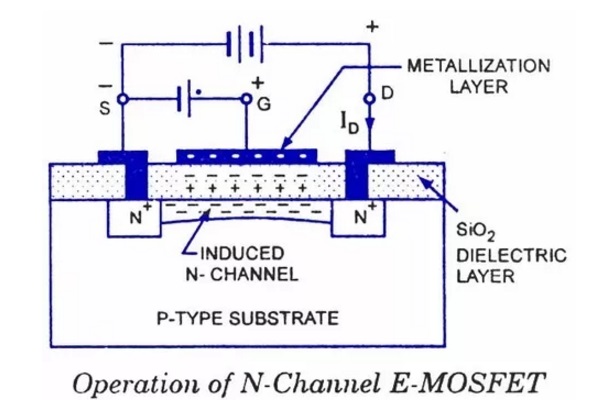
Figure-3 depicts construction of enhancement type MOSFET. It also mentions circuit symbol of N-channel MOSFET of enhancement type.Here continuous channel does not exist from source to drain. Hence no current flows at zero gate voltage.Symbol depicts broken channel between 'S' to 'D' terminals.
When positive voltage is applied to the gate, it will induce a channel by flowing minority carriers(i.e. electrons) fromP-type bulk into the concentrated layer.
Figure-4 depicts drain characteristics and transfer curve of enhancement type of MOSFET(N-channel).As shown in the figure-4 minimum threshold voltage is needed for the flow of drain current to start.
This type of FET is ideal for switching application. This is due to the fact that no gate voltage is needed to keepthe device in 'off' state. Moreover the device can be powered ON with the application of same polarity as drain terminal.
Following are the important comparison features between Depletion and Enhancement MOSFET types:
• Enhancement MOSFET does not conduct at 0 volt, as there is no channel in this type to conduct.Depletion MOSFET conducts at 0 volt. Moreover when positive cut-off gate voltage is applied to depletion MOSFET,hence it is less preferred.
• The depletion MOSFET does not have any kind of leakage currents such as gate oxide and sub threshold type.
• Depletion MOSFET logic operations are opposite to enhancement type of MOSFETs.
• Diffusion current(i.e. sub-threshold leakage current) exists in enhancement MOSFET whiledepletion MOSFET do not have any diffusion current.
Comparison between NMOS and PMOS types
Refer NMOS vs PMOS which mentions comparison between NMOS and PMOS type of MOSFETs.
Difference between JFET and MOSFET
Refer JUGFET vs MOSFET which mentions difference between JFET and MOSFET.
What is difference between
BJT vs FET
Diac vs Triac
LED vs Laser
Photo Diode vs Photo Transistor
Halfwave rectifier vs Fullwave rectifier
RF and Wireless Terminologies
Depletion Mode Mosfet N-channel
Share this page
Depletion Mode Mosfet Ltspice
Depletion Mode Mosfet Pedal Circuits
Translate this page
