Atomic Number Of Helium
Main Difference – Helium vs Hydrogen
Atomic Number: 2: Period: 1: Atomic Mass: 4.002602 amu (atomic mass unit) Color: Colorless: Crystal structure. Helium was the first element that was not. The atomic number of helium is 2. Helium has the distinction of being the only element discovered outside of Earth prior to finding it within our planet. The gas was first isolated from terrestrial sources in 1895 by the British chemist Sir William Ramsay, who discovered it in cleveite, a uranium-bearing mineral.
The known isotopes of helium contain from one to six neutrons, so their mass numbers range from three to eight. Of these six isotopes, only those with mass numbers of three (helium-3, or 3 He) and four (helium-4, or 4 He) are stable; all the others are radioactive, decaying very rapidly into other substances.
Hydrogen and Helium are the first two elements that are found in the periodic table of elements. Therefore, they are the smallest and lightest atoms on earth. Both of them are gaseous substances. Due to the characteristic features of hydrogen and helium, there are many applications of these gases in industry. Due to the very light weight of these gases, they are used to fill air balloons. The main difference between helium and hydrogen is that helium atom exists as a monoatomic gas in the atmosphere whereas hydrogen exists as a diatomic gas in the atmosphere.
Key Areas Covered
1.What is Helium
– Properties, Isotopes, Reactions, and Applications
2. What is Hydrogen
– Properties, Isotopes, Reactions, and Applications
3. What are the Similarities Between Helium and Hydrogen
– Outline of Common Features
4. What is the Difference Between Helium and Hydrogen
– Comparison of Key Differences
Key Terms: Atomic Mass, Atomic Number, Deuterium , Helium, Hydrogen, Isotopes of Helium, Protium, Tritium
What is Helium
Helium is an element that has the atomic number 2 and is a gaseous substance. The chemical symbol for helium is He. The electron configuration of helium is 1s2. The atomic symbol of helium is 42He. An atom of helium is composed of 2 protons and 2 neutrons in the nucleus along with 2 electrons in its 1s orbital. Therefore, the atomic mass of helium is 4.002602 amu. At room temperature and pressure, helium is a colorless and odorless gas. Helium is considered as the second most abundant element in the universe. It exists as a monoatomic gas.
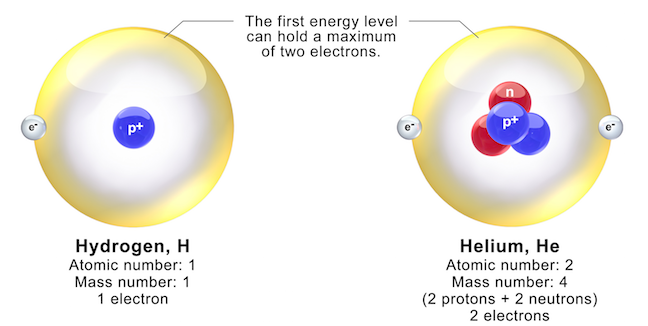
The melting point of helium is about -272.2oC, which is a very low value. The boiling point of helium is given as -268oC. This makes it a gas for a wider range of temperatures. In the periodic table of elements, helium is categorized as an s block element but is placed in the right side corner of the table. This is because helium is an inert gas that will not undergo chemical reactions. It is also a non-metal.
Since helium is a noble gas, it only shows zero oxidation state. There are two known isotopes of helium. They are 3He isotope and 4He isotope. 4He is the most abundant form among them and its abundance is given as 99%. Both of these isotopes are stable and no radioactive decay can be observed. However, there are some other isotopes as well. They are unstable and radioactive.
Helium is widely used in balloons. In addition, helium is used to provide a controlled atmosphere for many synthesis reactions (such as synthesis of silicon crystals) due to its high inertness. Nexus presets. It is also used as an inert shield for arc welding. Helium can be converted to its liquid form, which is known as liquid helium and is used as an important cryogenic material.
What is Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element having the atomic number 1 and is given in the symbol H. An atom of hydrogen is composed of one proton and no neutrons in the nucleus; it has one electron in its 1s orbital. The electron configuration of hydrogen is given as 1s1. Hydrogen is an s block element in the periodic table. The atomic weight of hydrogen is 1.00794 amu.
At room temperature and pressure, hydrogen exist as a diatomic gaseous molecule. It is a colorless and odorless gas. The melting point of hydrogen is about -259oC. The boiling point comes around -252oC. Hydrogen has three oxidation states. They are -1, 0 and +1. When hydrogen is attached to a metal atom, it has -1 oxidation state.
There are three major isotopes of hydrogen: Protium, Deuterium, and tritium. Protium is the most abundant isotope and has an abundance of 99%. Therefore, when we generally talk about hydrogen, we are talking about Protium. Deuterium is also a stable isotope but is less abundant. It has a neutron in its nucleus whereas Protium does not. Tritium is a radioactive isotope. Furthermore, there are many other isotopes that are not stable, and are highly radioactive.
There are many applications of hydrogen gas. Large quantities of hydrogen are used in the processing of fossil fuels. Hydrogen gas is also used in the production of ammonia. Moreover, hydrogen is used as a coolant in power plants as well.
Similarities Between Helium and Hydrogen
- Helium and Hydrogen are gaseous substances at standard temperature and pressure conditions.
- Both have only 1s orbital.
- Both are small and light substances.
- Both elements belong to the s block of the periodic table.
- Both are nonmetals.
Difference Between Helium and Hydrogen
Definition
Helium:Helium is an element having the atomic number 2 and is represented by the symbol He.
Hydrogen:Hydrogen is a chemical element having the atomic number 1 and is represented by the symbol H.
Atomic Number
Helium:The atomic number of helium is 2.
Hydrogen:The atomic number of hydrogen is 1.
Atomic Weight
Helium: The atomic weight of helium is 4.002602 amu.
Hydrogen: The atomic weight of hydrogen is 1.00794 amu.
Compounds
Helium: Beamng drive apk obb android. Helium exists as a monatomic gaseous substance.
Hydrogen:Hydrogen exists as a diatomic gaseous molecule.
Oxidation States
Helium: Helium has only 0 oxidation state.
Hydrogen: Hydrogen has -1, 0 and +1 oxidation states.
Isotopes
Helium:Helium has two major isotopes as 3He and 4He.
Hydrogen: Hydrogen has three major isotopes; Protium, deuterium, and tritium.
Melting Point
Helium:The melting point of helium is -272.2oC.
Hydrogen:The melting point of hydrogen is -259oC.
Conclusion
Helium and hydrogen are chemical elements that are mostly found in the atmosphere as gaseous substances due to their very low melting and boiling temperatures. The main difference between Helium and hydrogen is that helium atom exists as a monoatomic gas in the atmosphere whereas hydrogen exists as a diatomic gas in the atmosphere.
References:
1. “It’s Elemental.” It’s Elemental – The Element Helium. N.p., n.d. Web. Available here. 13 Aug. 2017.
2. “Hydrogen.” Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 13 Aug. 2017. Web. Available here. 13 Aug. 2017.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Blausen 0476 HeliumAtom” By BruceBlaus – Own work (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Blausen 0530 HydrogenIsotopes” By BruceBlaus – Own work (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present). The number of protons determines how many electrons surround the nucleus, and it is the arrangement of these electrons that determines most of the chemical behavior of an element.
In a periodic table arranged in order of increasing atomic number, elements having similar chemical properties naturally line up in the same column (group). For instance, all of the elements in Group 1A are relatively soft metals, react violently with water, and form 1+ charges; all of the elements in Group 8A are unreactive, monatomic gases at room temperature, etc. In other words, there is a periodic repetition of the properties of the chemical elements with increasing mass.
Number Of Protons For Helium

Atomic Number Of Helium-4
In the original periodic table published by Dimitri Mendeleev in 1869, the elements were arranged according to increasing atomic mass— at that time, the nucleus had not yet been discovered, and there was no understanding at all of the interior structure of the atom, so atomic mass was the only guide to use. Once the structure of the nucleus was understood, it became clear that it was the atomic number Abbyy lingvo x5 free. download full version. that governed the properties of the elements.
